|


|
 |


Note: Strong oxidizing reagents will oxidize benzylic alcohols and carbonyls to carboxylic acids
|
|
|


|
 |


Caution: Strong oxidizing reagents will oxidize benzylic alkyl groups even if no initial C-O bond exists
|
|
|


|
 |


Caution: Even with extended alkyl chains, the strong oxidizing agent will wipe out all of the substituent chains down to benzylic carboxylic acids
|
|
|


|
 |


Caution: Cr(IV) derived oxidizing reagents work to generate benzylic carboxylic acids as well. The difference is these are run under acidic conditions instead of basic
|
|
|


|
 |

Note: Benzylic oxidation requires the presence of at least one benzylic hydrogen, so tert-butyl benzene is resistant to oxidation.
|
|
|


|
 |


Note: Milder oxidant to oxidize benzylic alcohols to carbonyls
|
|
|
O](https://cdb.ics.uci.edu/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=C%5BC%40%40H%5D%28c1ccccc1%29O&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)

|
 |


Note: Milder oxidant to oxidize benzylic alcohols to carbonyls
|
|
|


|
 |

Note: Benzylic oxidation requires the presence of a benzylic hydrogen, so no reaction occurs here
|
|
|


|
 |

Note: This reagent only works on benzylic alcohols, not 'regular' alkyl alcohols
|
|
|


|
 |


Note: Clemmenen reduction converts aldehydes and ketones into alkanes under acidic conditions
|
|
|


|
![NN.[Na]O](https://cdb.ics.uci.edu/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=NN.%5BNa%5DO&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)
heat
 |


Note: Wolff-Kishner reduction converts aldehydes and ketones into alkanes under basic conditions
|
|
|
[O-]](https://cdb.ics.uci.edu/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=c1ccc%28cc1%29%5BN%2B%5D%28%3DO%29%5BO-%5D&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)

|
 |


Note: Nitro groups can be reduced to amino groups with H2 and a metal catalyst
|
|
|


|
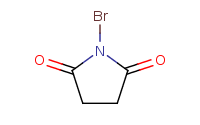
Light, Peroxide
 |


Note: Benzylic carbons can be brominated with NBS and peroxide, or Br2 and light
|
|
|
|
|
|
(0.105 sec)
Link
|
|